3D printing has revolutionized the way we create and manufacture objects. However, even the most experienced makers encounter challenges. Understanding 3D printing troubleshooting: 15 most common problems & solutions can significantly enhance your printing experience. Below, we delve into the most frequent issues and their effective solutions.
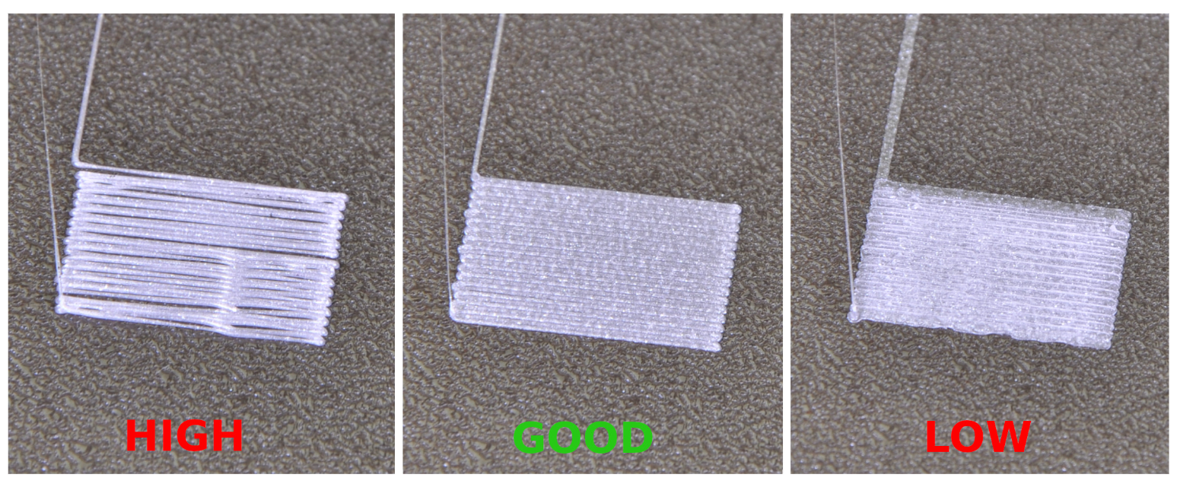
1. Warping
Warping occurs when the edges of a print lift off the build plate. This issue is often caused by rapid cooling of the material. To mitigate warping, consider the following:
- Use a heated bed to maintain temperature.
- Apply adhesive substances like glue stick or hairspray to the build surface.
- Ensure proper bed leveling before starting the print.
2. Layer Separation
Layer separation happens when the layers of a print do not adhere properly. This can be due to insufficient temperature or poor material quality. To address this:
- Increase the nozzle temperature slightly.
- Check the filament for moisture absorption.
- Adjust the print speed to allow better layer adhesion.
3. Stringing
Stringing refers to the fine strands of filament that appear between parts of a print. This is often a result of excessive oozing. To reduce stringing, you can:
- Enable retraction settings in your slicer software.
- Increase travel speed to minimize oozing during non-print moves.
- Lower the printing temperature slightly.
4. Under-extrusion
Under-extrusion occurs when the printer fails to deliver enough filament. This can lead to weak prints. To resolve under-extrusion:
- Check for clogs in the nozzle.
- Ensure the filament is of good quality and not tangled.
- Calibrate the extruder steps per millimeter.
5. Over-extrusion
Over-extrusion results in excess filament being laid down, causing blobs and zits on the print. Solutions include:
- Adjust the flow rate in your slicer settings.
- Reduce the nozzle temperature to improve filament flow.
- Check the filament diameter and adjust settings accordingly.
6. Poor Adhesion to the Build Plate
If prints do not stick to the build plate, they can shift or fail. To improve adhesion:
- Clean the build surface regularly.
- Use a different build surface material, such as PEI or glass.
- Adjust the first layer height for better contact.
7. Nozzle Clogs
Nozzle clogs can halt your printing process. Regular maintenance is key. Consider:
- Using a cleaning filament to clear the nozzle.
- Performing a cold pull to remove debris.
- Regularly checking for filament quality.
8. Print Quality Issues
Inconsistent print quality can stem from various factors. To enhance quality:
- Ensure your printer is properly calibrated.
- Use high-quality filament.
- Regularly maintain your printer components.
9. Filament Jamming
Filament jamming can disrupt your print job. To prevent this:
- Check the filament path for obstructions.
- Ensure the spool can rotate freely.
- Use a filament guide to reduce friction.
10. Electrical Issues
Electrical problems can lead to unexpected shutdowns. Regularly inspect:
- Wiring for wear and tear.
- Power supply connections.
- Firmware updates for your printer.
11. Temperature Fluctuations
Inconsistent temperatures can affect print quality. To stabilize temperatures:
- Use an enclosure to maintain ambient temperature.
- Calibrate temperature settings regularly.
- Monitor the thermistor for accuracy.
12. Incorrect Slicing Settings
Improper slicing can lead to various issues. Always double-check:
- Layer height and print speed settings.
- Infill percentage and pattern.
- Support structures for complex prints.
13. Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failures can halt printing. Regular maintenance is essential. Check:
- Belt tension and alignment.
- Lubrication of moving parts.
- Stepper motor functionality.
14. Software Glitches
Software issues can disrupt your workflow. To minimize glitches:
- Keep your slicing software updated.
- Regularly back up your settings.
- Consult forums for troubleshooting tips.
15. Lack of Knowledge
Finally, a lack of understanding can lead to frustration. To enhance your knowledge, consider:
- Joining online communities and forums.
- Reading comprehensive guides, such as the 3D Printing Troubleshooting Guide.
- Experimenting with different settings and materials.
In conclusion, mastering 3D printing troubleshooting: 15 most common problems & solutions can significantly improve your printing experience. By understanding these common issues and their solutions, you can enhance your skills and produce high-quality prints with confidence.






